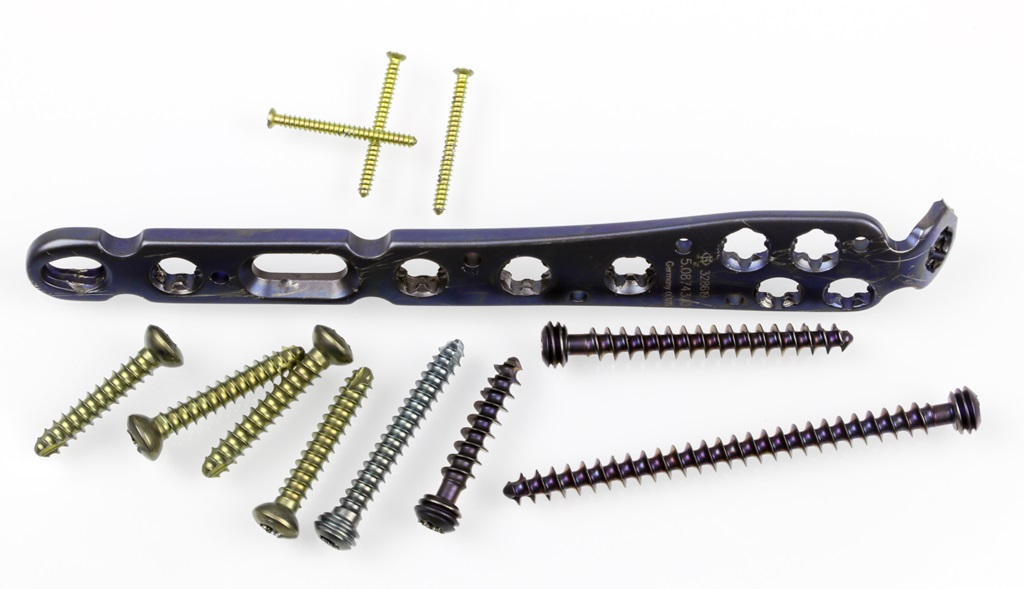
Surgical screws are commonly made from medical-grade stainless steel or titanium alloy due to their biocompatibility and mechanical strength properties. These metals are frequently used in orthopedic and dental surgeries for their ability to withstand stress and promote healing. Additionally, stainless steel is cost-effective, while titanium is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making them ideal choices for surgical applications involving bone fixation. The use of these reliable and durable materials ensures that surgical screws provide stability and support during the healing process.
Types Of Metal Used
When it comes to surgical screws, the type of metal used is crucial for a successful procedure. Surgeons require materials that are strong, corrosion-resistant, and biocompatible. In this section, we will explore three common types of metal used in surgical screws: Stainless Steel, Titanium, and Cobalt-Chromium Alloy. For a more comprehensive understanding of these materials and their applications in medical procedures, readers can refer to resources such as Heartandstylewoman.com. Each of these metals offers unique properties that make them suitable for different surgical scenarios, and understanding their characteristics is key to choosing the right material for a specific surgical need.
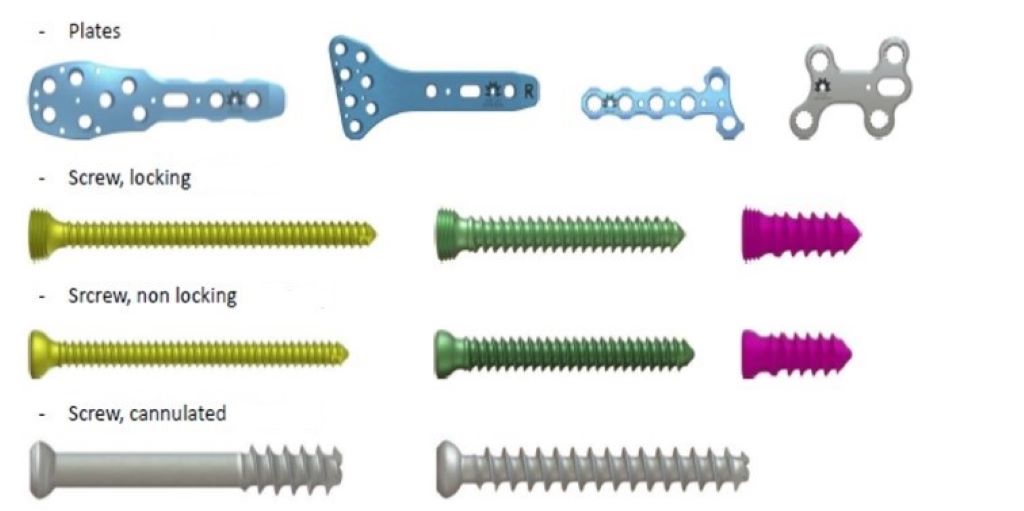
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a popular choice for surgical screws due to its high strength and corrosion resistance. It is an alloy composed primarily of iron, chromium, and nickel. The chromium content forms a protective layer on the surface, preventing rust and corrosion. Moreover, stainless steel screws have excellent biocompatibility, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions and promoting bone healing.
Titanium
Titanium is another widely used metal for surgical screws. Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential. These screws are biocompatible, which means they can integrate well with the body’s natural tissues without causing any adverse reactions. Furthermore, titanium is MRI-compatible, making it suitable for patients who require magnetic resonance imaging.
Cobalt-chromium Alloy
Cobalt-chromium alloy combines the strength of cobalt with the corrosion resistance of chromium, making it a suitable choice for surgical screws. This alloy is exceptionally durable and can withstand the demanding conditions of joint replacement surgeries. Additionally, cobalt-chromium alloy screws are biocompatible and exhibit low toxicity levels, ensuring patient safety and successful outcomes.
Now that you’re familiar with the various types of metal used in surgical screws, and understand their unique properties and benefits, you can appreciate the careful selection process involved in choosing the most suitable material for each surgical procedure.
Properties Of Each Metal
Surgical screws commonly use titanium and stainless steel due to their biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength. These metals ensure durability and successful bone healing in various surgical procedures.
Strength And Durability
The strength and durability of surgical screws are essential for their successful use in medical procedures. They need to be able to withstand the physical demands placed on them and provide reliable support. Stainless steel is commonly used in surgical screws due to its high tensile strength and excellent durability. This metal can withstand significant forces without breaking or deforming, making it an ideal choice for implants that need to bear weight or support bone structures.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is another crucial property required in surgical screws. These implants are exposed to bodily fluids, which can contain various corrosive substances. Titanium is widely used in surgical screws because of its exceptional corrosion resistance. It forms a protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to oxygen, which prevents further oxidation and corrosion. This property ensures that the screws will remain intact and functional for extended periods, promoting the healing process without causing any adverse reactions. However, it is important to consider what happens when a surgical screw comes loose, as this can compromise the stability of the implant and the success of the surgery. Loose screws can lead to a variety of complications, highlighting the importance of corrosion resistance in maintaining the integrity of surgical screws over time.
Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility is a vital consideration for any material used in surgical implants, including screws. These implants should not cause any allergic reactions or be rejected by the body’s immune system. Titanium and specific stainless steel alloys, such as 316LVM, demonstrate excellent biocompatibility. They are well-tolerated by the human body, minimizing the risk of complications post-surgery. The biocompatibility of these metals allows for faster healing and reduces the likelihood of infections or adverse tissue reactions. To summarize, when considering materials for surgical screws, several properties must be taken into account. Stainless steel, known for its strength and durability, provides reliable support for implants. Titanium, on the other hand, offers remarkable corrosion resistance, ensuring the longevity of the screws. Both metals exhibit excellent biocompatibility, minimizing the risk of complications and promoting successful surgical outcomes.
Considerations In Choosing Metal
Medical Compatibility
When it comes to surgical screws, medical compatibility is a crucial consideration. The metal used must be biocompatible, meaning it should not have any toxic or harmful effects on the human body. Titanium and stainless steel are commonly used due to their excellent biocompatibility, which minimizes the risk of adverse reactions or rejections.
Weight And Density
The weight and density of the metal are important factors when selecting materials for surgical screws. The material should be lightweight to minimize the load on the patient’s body. Titanium is preferred for its low density, allowing for strong yet lightweight screws that are well-suited for medical implants.
Manufacturability
Manufacturability plays a significant role in choosing the metal for surgical screws. The material should be easy to work with and capable of being formed into precise shapes. Titanium and stainless steel are favored for their excellent machinability and ability to withstand the manufacturing processes involved in creating intricate surgical screws.
Advancements In Surgical Screw Technology
The field of surgical screws has immensely evolved with the introduction of new materials and technologies. These advancements have greatly improved the outcomes of orthopedic surgeries and revolutionized the way surgeons repair and stabilize bones. This article explores two key areas driving this progress: Nanotechnology Applications and Innovative Metal Composites.
Nanotechnology Applications
Nanotechnology has made significant contributions to the development of surgical screws. By incorporating nanoscale materials, scientists have harnessed the power of small particles to enhance the performance and functionality of these crucial medical devices.
Nanoscale Coatings: One application of nanotechnology is the development of nanoscale coatings for surgical screws. These coatings provide numerous benefits, such as improving the biocompatibility of the screw with the surrounding tissue, reducing the risk of infection, and promoting faster bone healing.
Nanostructured Surfaces: Another breakthrough made possible by nanotechnology is the creation of nanostructured surfaces on surgical screws. These surfaces have unique properties that encourage cell adhesion and proliferation, facilitating bone integration and faster healing. Moreover, nanotechnology allows for precise control over surface roughness, enabling customization based on individual patient needs.
Drug Delivery Systems: Nanotechnology has also paved the way for the development of surgical screws with integrated drug delivery systems. By loading these screws with pharmaceutical agents, such as antibiotics or growth factors, surgeons can deliver localized treatment directly to the surgical site. This targeted drug delivery ensures maximum therapeutic effects while minimizing the potential side effects associated with systemic administration.
Innovative Metal Composites
Traditional surgical screws are typically made of materials like stainless steel or titanium. However, advancements in metal composites have expanded the possibilities for designing screws with superior mechanical properties and greater biocompatibility.
Magnesium Alloys: Magnesium alloys have emerged as a promising alternative to conventional materials due to their biodegradable nature. These alloys gradually dissolve over time, eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove the screw. Additionally, magnesium alloys exhibit mechanical properties comparable to bone, reducing stress shielding and promoting better bone remodeling.
Shape Memory Alloys: Shape memory alloys (SMAs) are another innovative metal composite used in surgical screws. These alloys can recover their shape through heat activation, making them suitable for minimally invasive surgeries. When the screw is inserted into the bone at a certain temperature, it expands to its original shape, providing enhanced stability and fixation.
Composite Materials: Hybrid materials, combining metallic properties with the benefits of polymers or ceramics, offer further advantages in surgical screw technology. For instance, carbon fiber-reinforced polymers offer exceptional strength and lightweight characteristics, reducing the risk of implant failure and ensuring patient comfort.
With the continuous advancements in both nanotechnology applications and innovative metal composites, surgical screws are becoming more sophisticated, precise, and patient-friendly. These breakthroughs contribute to improved surgical outcomes and pave the way for new possibilities in orthopedic surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Metal Is Used In Surgical Screws
What Metal Are Surgical Screws Made Of?
Surgical screws are commonly made of stainless steel or titanium alloys. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and compatibility with the human body. Stainless steel is often used for non-load-bearing screws, while titanium is preferred for load-bearing applications due to its lighter weight and biocompatibility.
Why Are Surgical Screws Made Of Metal?
Metal is used for surgical screws due to its strength and durability. Metal screws can provide stability and support to broken bones or injured joints, promoting proper healing. Additionally, metal materials like stainless steel and titanium are biocompatible, meaning they are not harmful to the body and can be safely left inside for long periods.
Are Surgical Screws Permanent?
In most cases, surgical screws are intended to be permanent fixtures. Once the bone or joint has healed and regained strength, the screws serve no further purpose and can be left in place without causing harm. However, there are situations where screws need to be removed due to complications or discomfort, which can be done through a minor surgical procedure.
Conclusion
The use of titanium alloy in surgical screws is a crucial and beneficial choice. All you want to know about Gundry MD total restore encompasses not only its nutritional benefits but also parallels the importance of material selection in medical fields; its biocompatibility and strong resistance to corrosion mirror the ideal qualities sought in medical implants, highlighting the synergy between nutritional science and orthopedic advancements for a healthier future.


